Summary
The transition from automation to augmentation represents a pivotal shift in the role of Artificial Intelligence (AI) within the workplace. This evolution is marked by a move away from AI systems that merely replicate human tasks, towards those that enhance and expand human capabilities. Automation has traditionally focused on cost reduction and efficiency by replacing repetitive, low-skill tasks with AI systems (Source 1). However, the next phase emphasizes augmentation, where AI acts as a collaborative partner to humans, providing tools and insights that enhance decision-making and creative problem-solving processes (Source 2).
In this augmented framework, AI systems are designed to leverage human strengths and complement areas where AI excels, such as data processing and pattern recognition. This synergy is expected to foster Innovation and drive productivity, as employees are empowered to focus on higher-level, strategic activities (Source 3). The integration of AI as an augmentative tool also encourages a more dynamic and adaptive workforce, where continuous learning and skill development become central to organizational success (Source 4).
Moreover, this shift towards augmentation necessitates a reevaluation of job roles and workplace structures. Companies are increasingly investing in training and development programs to equip workers with the skills necessary to work alongside AI technologies effectively (Source 5). This approach not only mitigates fears of job displacement but also highlights the potential for AI to create new roles and opportunities within the workforce (Source 6).
In summary, the journey from automation to augmentation in workplaces underscores a transformative approach where AI is not just a tool for efficiency but a catalyst for human potential and creativity. This paradigm shift is poised to redefine how organizations operate, fostering environments where AI and human intelligence coalesce to unlock new levels of productivity and innovation.
Introduction
In recent years, the pervasive influence of artificial intelligence (AI) in workplaces has shifted from a focus on automation to a more nuanced role of augmentation. Initially, AI’s primary application was to automate repetitive and mundane tasks, streamlining processes and enhancing efficiency (Source 1). This phase of AI deployment was characterized by the replacement of human labor in sectors where routine tasks could be executed more swiftly and accurately by machines. However, as AI technologies have matured, the narrative is evolving towards a more collaborative approach where AI and human capabilities are integrated to complement each other.
The concept of augmentation emphasizes AI’s potential to enhance human abilities rather than replace them. This transition is driven by advancements in Machine Learning, natural language processing, and data analytics, enabling AI systems to understand and interact with complex human-centric tasks (Source 2). By augmenting human effort, AI can provide valuable insights, boost productivity, and support decision-making processes, thereby unlocking new levels of innovation and performance within organizations.
Moreover, this paradigm shift underscores the importance of re-skilling and up-skilling the workforce to adapt to new collaborative roles alongside AI systems. As AI takes on more sophisticated functions, employees are required to develop new skills that focus on creativity, emotional intelligence, and problem-solving—areas where humans excel and AI still lags (Source 3). This symbiotic relationship between AI and human workers aims to create a more dynamic and adaptive work environment.
In summary, the evolution from automation to augmentation marks a significant transformation in how AI is perceived and utilized in the workplace. It reflects a broader trend towards harnessing AI’s capabilities to empower human workers and foster a more innovative and efficient workforce. As businesses continue to explore this new phase of AI integration, the potential for augmented collaboration holds promise for both productivity and job satisfaction (Source 4).
Understanding the Evolution of AI in Workplaces
The evolution of AI in workplaces has been a transformative journey marked by significant milestones, each reshaping the landscape of work. Initially, the focus was on automation, where AI technologies were primarily deployed to perform repetitive and mundane tasks more efficiently than humans. This phase was characterized by the development of rule-based systems and robotic process automation (RPA), which allowed organizations to streamline operations and reduce human error (Source 1).
As AI technologies matured, they began to encompass more sophisticated capabilities, including machine learning and natural language processing. These advancements enabled AI to handle more complex tasks that required a degree of cognitive function, such as Data Analysis and predictive modeling. This shift marked the beginning of AI’s role not only as a tool for operational efficiency but also as a strategic asset for decision-making (Source 2).
The current phase of AI’s evolution in workplaces is characterized by augmentation, where AI systems are designed to complement and enhance human capabilities rather than replace them. This approach leverages AI’s strengths in data processing and pattern recognition to assist humans in tasks that require creativity, emotional intelligence, and nuanced judgment. For instance, AI can analyze vast datasets to generate insights that inform human decision-making, allowing employees to focus on strategic and creative aspects of their roles (Source 3).
Moreover, the integration of AI into workplaces is fostering new forms of collaboration between humans and machines. By understanding and anticipating human needs, AI systems are becoming more intuitive, providing tailored support that enhances productivity and innovation (Source 4). This evolution reflects a broader shift towards a more symbiotic relationship between humans and technology, where AI serves as a partner in achieving common goals.
The Shift from Automation to Augmentation
The transition from automation to augmentation marks a significant evolution in the role of artificial intelligence (AI) within workplaces. While automation focuses on replacing human tasks with machine efficiency, augmentation seeks to enhance human capabilities, fostering a collaborative environment where AI and humans work in tandem. This shift is driven by the recognition that while machines excel at processing large amounts of data and performing repetitive tasks, human intuition, creativity, and emotional intelligence are irreplaceable (Source A).
In the past, automation was primarily associated with streamlining operations, reducing costs, and improving efficiency by taking over routine and mundane tasks. However, as AI technologies have advanced, there is a growing emphasis on augmentation—using AI to empower employees to perform their roles more effectively. This involves deploying AI tools that assist in decision-making, provide insights from complex data sets, and facilitate more personalized customer interactions (Source B).
The augmentation approach aligns with the evolving needs of modern workplaces, which demand adaptability and innovation. AI systems can analyze vast amounts of information rapidly, offering insights that humans might overlook, thereby enhancing decision-making processes. In creative industries, AI can generate ideas or prototypes, allowing human workers to focus on refining and innovating (Source C).
Moreover, augmentation fosters a more inclusive work environment. By relieving employees of tedious tasks, AI enables them to concentrate on more strategic and fulfilling work, potentially improving job satisfaction and productivity. This shift also necessitates a rethinking of job roles and skills, emphasizing the development of digital literacy and the ability to work alongside AI systems (Source D).
Ultimately, the shift from automation to augmentation represents a paradigm change in how we perceive technology in the workplace. It underscores the potential of AI not just as a tool for efficiency, but as a partner in creativity and innovation, enhancing human potential rather than replacing it.
The Role of Automation in Today’s Workplaces
Automation plays a transformative role in today’s workplaces, reshaping industries by enhancing productivity, reducing operational costs, and improving efficiency. In many sectors, automation has become integral to daily operations, driving significant changes in how tasks are performed and how businesses operate.
One of the primary roles of automation is in streamlining repetitive and mundane tasks. By replacing manual processes with automated systems, organizations can free up human resources for more strategic and creative endeavors. For instance, in sectors such as manufacturing, automated machinery and robotics are used to perform tasks that are dangerous or monotonous for human workers, thereby enhancing safety and efficiency (Source A).
Moreover, automation is pivotal in data management and analysis. In today’s data-driven world, businesses generate and process vast amounts of information. Automation tools, such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms, help in efficiently managing this data, providing valuable insights that drive decision-making and strategic planning (Source B). This not only speeds up processes but also minimizes the risk of human error, ensuring accuracy and reliability in operations.
Furthermore, automation facilitates better customer service through tools like chatbots and automated response systems. These tools can handle routine inquiries and transactions, allowing customer service representatives to focus on complex issues that require human intervention (Source C).
However, the role of automation is not without challenges. It necessitates a shift in workforce skills, requiring employees to adapt to new technologies and develop digital competencies. This has led to a growing emphasis on continuous learning and development within organizations to ensure employees remain relevant and competitive in an increasingly automated world (Source D).
Overall, automation is a critical component of modern workplaces, driving efficiency and innovation while also presenting new challenges and opportunities for workforce development.
Benefits and Limitations of Automation
Automation in the workplace offers a plethora of benefits that have been widely recognized across various industries. Primarily, automation enhances productivity by performing repetitive and mundane tasks more efficiently than human workers, allowing employees to focus on more strategic and creative aspects of their jobs (Source 1). This shift not only boosts overall productivity but also increases job satisfaction as workers engage in more meaningful tasks. Furthermore, automation can significantly reduce operational costs by minimizing the need for manual labor and reducing the likelihood of human error, leading to higher accuracy and consistency in outputs (Source 2).

Another key advantage of automation is its ability to operate 24/7 without fatigue, which is particularly beneficial in sectors like manufacturing and customer service where continuous operation is crucial (Source 3). Additionally, automation technologies can enhance workplace safety by taking over dangerous tasks, thereby reducing the risk of workplace injuries (Source 4).
Despite these advantages, automation is not without its limitations. One of the primary concerns is the potential for job displacement, as machines and algorithms can replace human roles, especially in low-skilled positions (Source 5). This displacement can lead to significant socio-economic challenges, including increased unemployment and income inequality. Moreover, the initial implementation of automation technologies can be costly and time-consuming, requiring significant investment in infrastructure and training (Source 6).
Another limitation is the lack of flexibility; automated systems are typically designed for specific tasks and may struggle with handling exceptions or adapting to changes in the environment (Source 7). Additionally, over-reliance on automation can lead to a reduction in human oversight, potentially resulting in critical oversights if the system fails or is improperly configured (Source 8).
In conclusion, while automation presents undeniable benefits in terms of efficiency, cost savings, and safety, it is essential to balance these with the associated limitations to ensure a harmonious integration into the workplace.
Key Industries Impacted by Automation
Automation has been steadily reshaping industries across the globe, with certain sectors experiencing more profound transformations than others. The manufacturing industry, historically a forerunner in adopting automation, continues to see significant advancements with the integration of AI-driven robotics and smart technologies. These innovations not only enhance production efficiency but also enable predictive maintenance and quality control, minimizing downtime and reducing costs (Source 1).
The logistics and supply chain sector is another key industry impacted by automation. Here, AI technologies optimize routing and inventory management, ensuring faster and more reliable deliveries. Automated warehouses, equipped with autonomous vehicles and robotic systems, are becoming increasingly common, allowing for seamless operations and reduced human error (Source 2).
In the realm of healthcare, automation is driving change through AI-powered diagnostic tools and robotic surgery. These technologies enhance precision and speed in medical procedures, improving patient outcomes while alleviating the workload on healthcare professionals. Furthermore, administrative tasks within healthcare settings are being automated, streamlining operations and allowing staff to focus more on patient care (Source 3).
The financial services industry is also undergoing substantial transformation due to automation. AI algorithms now handle complex trading operations and risk assessments, providing faster and more accurate insights. Additionally, automation in the form of chatbots and virtual assistants is revolutionizing customer service, offering 24/7 support and freeing up human resources for more complex tasks (Source 4).
Retail is not left behind, as automation impacts everything from inventory management to personalized marketing strategies. Automated checkout systems and AI-driven analytics provide retailers with valuable insights into consumer behavior and preferences, enabling more targeted marketing efforts (Source 5).
Overall, while automation brings efficiency and innovation, it also necessitates a shift towards workforce augmentation, where human skills are complemented by AI capabilities to address the evolving demands of these industries.
What is Augmentation in the Context of AI?
Augmentation in the context of AI refers to the collaborative interaction between humans and artificial intelligence systems, where AI tools enhance human capabilities rather than replace them. This concept shifts the narrative from AI as a substitute for human labor to AI as a partner that amplifies human skills and decision-making processes.
In practical terms, augmentation involves AI systems taking on routine, repetitive tasks, thereby freeing humans to focus on more complex, creative, and high-value activities. For instance, in industries like healthcare, AI can assist by analyzing medical images with high precision, allowing doctors to spend more time on patient care and treatment planning (Source 1). Similarly, in finance, AI can handle massive datasets to detect patterns and predict market trends, enabling financial analysts to make more informed strategic decisions (Source 2).
The augmentation model leverages the strengths of both humans and machines. AI excels at processing vast amounts of data quickly and accurately, while humans bring to the table critical thinking, empathy, and ethical judgment. This synergy can lead to improved productivity, innovation, and job satisfaction as employees engage in tasks that require uniquely human traits, such as problem-solving and interpersonal interaction (Source 3).
Moreover, by promoting human-AI collaboration, organizations can foster a more inclusive work environment. Employees at all levels can engage with advanced technologies, democratizing access to AI-driven insights and tools. This empowerment through augmentation not only enhances individual performance but also drives organizational growth by encouraging continuous learning and adaptation in an ever-evolving technological landscape (Source 4).
Overall, augmentation represents a balanced approach where AI acts as an enabler, enhancing human capabilities and leading to a more dynamic and resilient workforce.
Defining Augmentation
Augmentation in the context of artificial intelligence (AI) refers to the use of technology to enhance and complement human skills rather than replacing them. Unlike automation, which focuses on the complete transfer of tasks from humans to machines, augmentation aims to create a synergistic relationship where AI tools empower employees to perform their jobs more efficiently and creatively (Source 1). This concept is rooted in the belief that while machines excel at processing and analyzing vast amounts of data, they cannot replicate the nuanced decision-making, emotional intelligence, and innovative thinking inherent to humans (Source 2).
The goal of augmentation is to leverage AI to enhance human capabilities, allowing workers to focus on higher-value tasks that require critical thinking and personal interaction. For instance, in fields like healthcare, AI can assist doctors by analyzing medical images or patient data more quickly and accurately than a human could alone, but the final diagnosis and treatment decisions are left to the clinician, who can interpret the data within the broader context of patient care (Source 3).
Moreover, augmentation is not limited to individual productivity but extends to improving team dynamics and collaborative efforts within organizations. AI tools can facilitate better communication and coordination among team members by managing workflows and providing real-time insights into project progress, thereby enabling teams to operate more cohesively (Source 4).
In essence, augmentation redefines the role of AI in the workplace from a substitute to a partner, fostering an environment where technology and human ingenuity coexist. This approach not only preserves the unique contributions of human workers but also enhances them, leading to more innovative and adaptive organizations (Source 5).
How Augmentation Differs from Automation
Augmentation and automation, though often intertwined in discussions about artificial intelligence (AI) in the workplace, serve fundamentally different roles and purposes. Automation focuses on replacing human labor with machines to perform repetitive and routine tasks, thereby enhancing efficiency and reducing costs. It is driven by the goal of minimizing human intervention in processes that can be handled by technology with precision and consistency (Source 1).
In contrast, augmentation is about enhancing human capabilities and decision-making processes rather than replacing them. It involves using AI tools to empower workers by providing them with insights, recommendations, and support that improve their productivity and creativity. Augmentation leverages AI to handle complex data analysis, thereby allowing humans to focus on higher-order tasks such as strategic planning and problem-solving, which require emotional intelligence, creativity, and contextual understanding (Source 2).
One of the key differences is the role of human agency. While automation tends to sideline human involvement, augmentation places humans at the center of the process, using AI as a collaborative partner rather than a replacement. This approach fosters a symbiotic relationship where AI complements human skills, allowing for a more dynamic and flexible work environment (Source 3).
Moreover, augmentation can lead to job enrichment rather than job displacement. As machines take on data-heavy tasks, employees are free to pursue more meaningful and engaging work, leading to increased job satisfaction and innovation. This transition reflects a shift in how organizations perceive technology—not as a threat to employment but as a tool that can elevate human potential and drive organizational growth (Source 4).
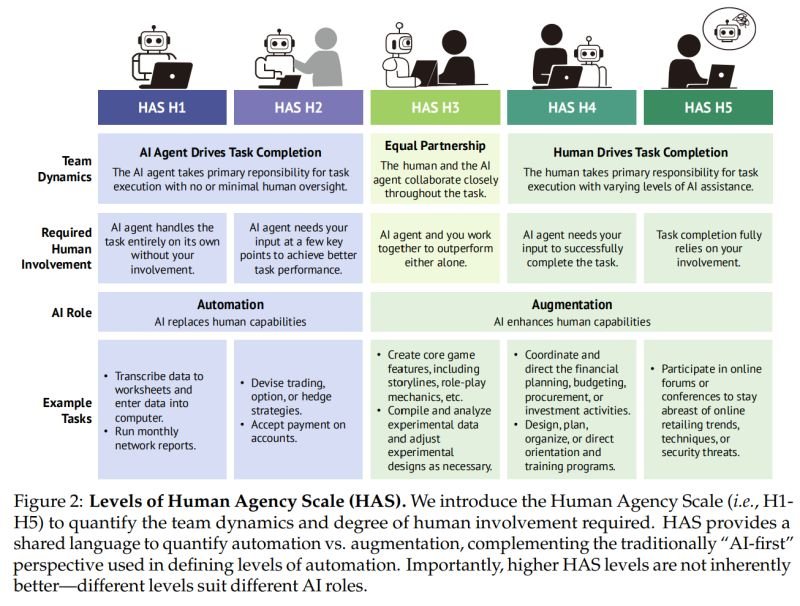
The Benefits of Augmentation in Workplaces
Augmentation in workplaces, where artificial intelligence (AI) technologies enhance human capabilities rather than replace them, offers a myriad of benefits that can transform how organizations operate and thrive. One of the primary advantages is increased productivity. By leveraging AI tools to handle repetitive and time-consuming tasks, employees can focus on more strategic, creative, and complex responsibilities that require human intuition and decision-making (Source 1). This shift not only boosts efficiency but also enhances job satisfaction as employees engage in more meaningful work.
Moreover, augmentation supports improved decision-making processes. AI systems can process vast amounts of data at high speeds, providing insights and analytics that humans alone cannot achieve. By augmenting human intelligence with AI-driven data analysis, organizations can make more informed, accurate, and timely decisions (Source 2). This capability is particularly valuable in industries such as finance, healthcare, and logistics, where real-time data and predictive analytics are crucial.
Additionally, augmentation fosters innovation by enabling employees to experiment and explore new ideas with the support of AI. With AI handling routine tasks, employees have more time and resources to dedicate to innovation and development, leading to the creation of new products, services, and business models (Source 3). This environment of creativity and innovation can give companies a competitive edge in rapidly changing markets.
Furthermore, augmentation enhances collaboration by providing tools that facilitate better communication and coordination among teams. AI-powered platforms can streamline workflows and enable seamless information sharing, which is essential for effective teamwork, especially in remote and hybrid work settings (Source 4).
In summary, the integration of AI augmentation in workplaces not only enhances productivity and decision-making but also stimulates innovation and collaboration, ultimately leading to a more dynamic and competitive business environment.
Enhancing Human Capabilities
The integration of AI into workplaces is not merely about replacing human roles but rather enhancing human capabilities, allowing employees to perform their tasks more efficiently and effectively. AI technologies, such as machine learning and natural language processing, can process and analyze vast amounts of data much faster than humans, providing insights that empower workers to make better-informed decisions (Source 1).
For instance, AI can augment human capabilities by automating routine tasks, thereby freeing up time for employees to focus on more strategic and creative aspects of their jobs. This shift allows workers to leverage their unique human skills, such as critical thinking, problem-solving, and emotional intelligence, which machines cannot replicate (Source 2). By handling repetitive and time-consuming tasks, AI enables employees to concentrate on high-value activities that require human judgment and intuition.
Moreover, AI tools can serve as decision-support systems, offering recommendations based on data analytics that humans might overlook. These tools can help employees identify patterns and trends, predict outcomes, and optimize processes, enhancing their ability to strategize and innovate (Source 3). For example, in sectors like healthcare, AI can assist doctors by analyzing medical data to suggest potential diagnoses or treatment plans, thereby augmenting the physicians’ expertise and improving patient outcomes (Source 4).
Furthermore, AI-driven platforms can facilitate personalized learning and development by identifying skill gaps and recommending targeted training programs. This approach not only helps employees enhance their current capabilities but also prepares them for future roles in an evolving job market (Source 5). Ultimately, the augmentation of human capabilities through AI fosters a collaborative environment where technology and human intelligence work hand in hand to achieve greater productivity and innovation.
Improving Decision-Making Processes
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is increasingly transforming decision-making processes within workplaces by providing tools that enhance human capabilities rather than replace them. The integration of AI into decision-making frameworks allows organizations to leverage vast amounts of data, offering insights that were previously inaccessible. AI systems can process and analyze data at speeds and precision beyond human capacity, identifying patterns and trends that inform more strategic decisions (Source A).
One of the primary advantages of AI in decision-making is its ability to reduce the cognitive load on human managers. By automating routine analysis tasks, AI frees up time for decision-makers to focus on more complex, nuanced problems that require human intuition and creativity. For instance, AI can quickly sift through data to highlight potential risks or opportunities, allowing managers to concentrate on devising strategic responses (Source B).
Furthermore, AI enhances the objectivity of decisions by minimizing biases that often skew human judgment. Algorithms can be designed to evaluate data based purely on statistical significance, reducing the influence of subjective biases in decision-making processes. This leads to more equitable outcomes, particularly in areas such as hiring, promotions, and performance evaluations, where unconscious biases can have significant impacts (Source C).
AI systems also facilitate real-time decision-making by providing timely insights through predictive analytics. This capability is crucial in fast-paced environments, where the ability to make informed decisions quickly can provide a competitive advantage. For example, in supply chain management, AI can predict demand fluctuations and optimize inventory levels, helping businesses reduce costs and improve service delivery (Source D).
In conclusion, AI’s role in improving decision-making processes is not about replacing human judgment but augmenting it. By providing enhanced data analysis capabilities, reducing biases, and enabling real-time insights, AI empowers managers to make better, more informed decisions that drive organizational success.
Fostering Innovation and Creativity
In the evolving landscape of artificial intelligence within workplaces, fostering innovation and creativity stands as a pivotal aspect of transitioning from automation to augmentation. AI’s role is no longer confined to streamlining repetitive tasks; it is now a catalyst for unlocking human potential by augmenting creative processes and driving innovation.
AI tools are increasingly being used to generate new ideas, design novel solutions, and explore uncharted territories in various fields. By analyzing vast datasets and identifying patterns, AI can provide insights that inspire human creativity, pushing the boundaries of what is possible (Source A). For instance, in design and arts, AI algorithms can suggest innovative concepts by merging different styles or predicting trends, thus enabling designers and artists to experiment with fresh perspectives and approaches (Source B).
Moreover, AI’s ability to process and synthesize information from diverse sources allows it to become a powerful brainstorming partner for humans. It can present a multitude of possibilities that might not be immediately apparent, thereby sparking innovative thinking (Source C). This collaborative dynamic between humans and machines facilitates a more profound exploration of ideas, where AI acts as an enabler rather than a replacement.
The integration of AI in creative processes also democratizes innovation by making sophisticated tools accessible to a broader audience, regardless of their technical expertise. This accessibility fosters a culture of creativity across all levels of an organization, encouraging individuals to contribute to innovation without the constraints of traditional skill barriers (Source D).
Ultimately, the augmentation of human creativity with AI not only enhances productivity but also cultivates an environment where innovative ideas can flourish, driving businesses towards unprecedented growth and success in an increasingly competitive market. As AI continues to evolve, its role in fostering innovation and creativity will be crucial for organizations aiming to remain at the forefront of their industries (Source E).
Case Studies: Successful AI Augmentation in Various Industries
In recent years, numerous industries have successfully integrated AI augmentation to enhance productivity and innovation. In the healthcare sector, AI has been pivotal in augmenting diagnostic processes. For instance, radiologists now employ AI systems to analyze medical images with remarkable precision, significantly reducing the time needed for diagnosis and allowing healthcare professionals to focus on complex patient care (Source 1). This combination of AI and human expertise is not only increasing accuracy but also improving patient outcomes.
The financial industry has also seen transformative benefits from AI augmentation. In banking, AI algorithms are utilized to detect fraudulent activities by analyzing transaction patterns in real-time. This has enabled financial institutions to prevent billions in losses while allowing human analysts to concentrate on strategic decision-making and customer service (Source 2). Furthermore, AI-driven chatbots are augmenting customer service by handling routine inquiries, freeing up human agents to tackle more intricate customer needs.
In the manufacturing sector, AI augmentation is streamlining operations through predictive maintenance. By analyzing data from machinery sensors, AI systems can predict equipment failures before they occur, minimizing downtime and reducing costs. This proactive approach allows engineers to focus on optimizing production processes rather than merely reacting to breakdowns (Source 3).
Retail is another industry benefiting from AI augmentation, where AI tools analyze consumer data to personalize shopping experiences, thereby increasing sales and customer satisfaction. Retailers are using AI to adjust inventory based on predictive analytics, ensuring they meet consumer demand efficiently (Source 4).
These case studies illustrate the profound impact of AI augmentation across various industries, demonstrating that when AI is used to complement human capabilities, it not only enhances efficiency but also fosters innovation and growth.
Healthcare: Augmenting Medical Diagnoses
In the realm of healthcare, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) is set to revolutionize the process of medical diagnoses by augmenting, rather than replacing, the capabilities of healthcare professionals. AI systems are being designed to assist doctors by providing more accurate and timely diagnoses, thus improving patient outcomes and optimizing the workflow within healthcare facilities.
AI technologies, such as machine learning and deep learning, are being utilized to analyze vast amounts of medical data, including electronic health records, imaging results, and genetic information, to identify patterns and potential anomalies that may not be immediately apparent to human practitioners (Source 1). For example, AI algorithms in radiology can effectively examine medical images, such as X-rays and MRIs, to detect early signs of diseases like cancer, often with a level of precision that rivals or even surpasses that of human radiologists (Source 2). This capability not only aids in early detection but also helps reduce the incidence of misdiagnoses, which can have serious implications for patient health.
Moreover, AI is playing a crucial role in personalizing treatment plans. By analyzing a patient’s unique data, AI can suggest tailored treatment options that align with the individual’s specific health needs and genetic makeup, thereby enhancing the efficacy of interventions (Source 3). This level of personalization ensures that patients receive the most appropriate care, potentially improving recovery rates and reducing the likelihood of adverse reactions to treatments.
While AI serves as a powerful tool to augment medical diagnoses, it is important to emphasize that it functions best in collaboration with human expertise. Healthcare professionals’ judgment, empathy, and ethical considerations remain indispensable, ensuring that AI-driven insights are applied effectively and compassionately in patient care (Source 4). This synergy between AI and human clinicians represents a promising advancement in the pursuit of improved healthcare delivery.
Finance: Enhancing Risk Assessment
The finance sector has long been at the forefront of adopting technology to streamline operations and enhance decision-making. With the advent of advanced AI technologies, the focus is shifting from automation to augmentation, particularly in the realm of risk assessment. Traditionally, risk assessment in finance relied on historical data analysis, which, while effective, often lacked the ability to predict unprecedented events or account for complex interdependencies within financial systems. AI is poised to transform this landscape by offering more nuanced insights and predictive capabilities.
One of the primary ways AI enhances risk assessment is through the integration of machine learning algorithms that can analyze vast amounts of data in real-time. These algorithms can identify patterns and correlations that human analysts might miss, providing a more comprehensive view of potential risks (Source 1). For instance, AI systems can process news articles, social media trends, and market data simultaneously to gauge market sentiment, which is vital for predicting stock market fluctuations and assessing credit risk (Source 2).
Moreover, AI-driven models are not just reactive but also predictive. They utilize predictive analytics to forecast future risks based on current trends, enabling financial institutions to implement proactive measures rather than merely responding to risks as they occur (Source 3). This capability is crucial for identifying emerging risks, such as those related to cybersecurity threats or climate change impacts on asset values.
Another significant advantage of AI in risk assessment is its ability to personalize risk profiles. By analyzing customer behavior and financial habits, AI can tailor risk assessments to individual clients, offering more accurate credit scoring and investment advice (Source 4). This personalization not only enhances customer satisfaction but also reduces the likelihood of default, benefiting both the client and the institution.
In summary, AI is revolutionizing risk assessment in finance by providing deeper insights, predictive capabilities, and personalized risk profiles, ultimately contributing to more informed decision-making and a more resilient financial system.
Manufacturing: Improving Quality Control
In the realm of manufacturing, the integration of AI technologies is revolutionizing quality control processes, moving beyond traditional automation to a more sophisticated augmentation of human capabilities. AI-driven quality control systems are now employing advanced machine learning algorithms and computer vision to enhance the accuracy and efficiency of defect detection and product inspection.
One of the primary advantages of AI in quality control is its ability to process vast amounts of visual and operational data at speeds and accuracies far surpassing human capabilities. For instance, AI systems equipped with high-resolution cameras and sensors can continuously monitor production lines, identifying defects such as surface imperfections or dimensional inaccuracies in real-time (Source 1). This not only reduces the likelihood of defective products reaching consumers but also minimizes the need for costly manual inspections.
Moreover, AI technologies are capable of learning from historical defect data to predict potential quality issues before they occur. By analyzing patterns and trends in production data, AI can provide predictive insights that allow manufacturers to address root causes proactively, thereby enhancing overall product quality and reducing waste (Source 2). This predictive maintenance approach helps in optimizing production processes and extending the lifespan of machinery by identifying anomalies that might indicate equipment failure.
Additionally, AI-driven quality control systems facilitate the customization of quality parameters to meet specific industry standards and customer requirements. This flexibility is crucial for manufacturers producing a wide range of products with varying quality specifications (Source 3). By augmenting human inspectors with AI tools, manufacturers can achieve a higher level of precision and consistency in quality control, leading to improved customer satisfaction and competitive advantage in the marketplace.
In summary, AI is transforming quality control in manufacturing by providing real-time defect detection, predictive maintenance capabilities, and customized quality management, thereby augmenting human expertise and driving operational excellence.
Challenges and Considerations in Implementing AI Augmentation
Implementing AI augmentation in workplaces introduces several challenges and considerations that organizations must navigate to optimize benefits while minimizing potential drawbacks. One of the primary challenges is the integration of AI systems with existing workflows and technologies. This often requires significant investment in infrastructure and can disrupt current operations if not managed carefully (Source 1). Moreover, organizations must ensure that AI systems are adaptable and can evolve alongside changing business needs and technological advancements (Source 2).
Data privacy and security are paramount concerns. As AI systems often require vast amounts of data to function effectively, safeguarding this data becomes crucial to prevent breaches and maintain trust with clients and employees (Source 3). Establishing robust data governance frameworks is essential to protect sensitive information while complying with regulatory requirements.
Another critical consideration is the potential impact on the workforce. While AI augmentation aims to enhance human capabilities, there is a risk of job displacement or significant changes in job roles. Organizations must prioritize reskilling and upskilling initiatives to empower employees to work alongside AI, thereby fostering a culture of continuous learning and adaptation (Source 4).
Ethical considerations also play a significant role. AI systems must be designed and implemented with transparency and fairness to prevent biases and ensure equitable outcomes. Organizations should establish ethical guidelines and oversight mechanisms to monitor AI deployments and address any unintended consequences (Source 5).
Finally, fostering collaboration between humans and AI requires a cultural shift within organizations. Leadership must actively promote an environment where AI is seen as a tool for empowerment rather than a threat, encouraging open dialogue and collaboration across all levels of the organization (Source 6). Addressing these challenges thoughtfully can pave the way for successful AI augmentation in workplaces.
Ethical Concerns and Bias in AI
As AI systems become increasingly integrated into workplace environments, ethical concerns and bias present significant challenges that must be addressed to ensure equitable and fair outcomes. One of the primary ethical concerns is the potential for AI to perpetuate or even exacerbate existing biases. AI systems often learn from historical data, which can reflect societal prejudices. If not carefully managed, these biases can be encoded into the AI’s decision-making processes, leading to discriminatory outcomes (Source 1).
For instance, AI-driven recruitment tools have been criticized for favoring certain demographics over others, reflecting biases present in historical hiring data (Source 2). Such biases can lead to exclusionary practices that disproportionately affect underrepresented groups, thereby perpetuating inequality in the workplace. Addressing these biases requires a concerted effort to ensure that AI models are trained on diverse and representative datasets. Moreover, the development of robust auditing processes to identify and mitigate bias is crucial (Source 3).
Another ethical concern is the transparency and accountability of AI systems. Many AI algorithms operate as “black boxes,” providing little insight into how decisions are made. This lack of transparency can hinder accountability, making it difficult to challenge or review decisions that negatively impact individuals (Source 4). To address this, there is a growing call for “explainable AI,” which aims to make AI decision-making processes more transparent and understandable to human users (Source 5).

Furthermore, the ethical use of AI in workplaces requires considerations of privacy and consent, particularly in scenarios where AI systems monitor employee activities. Striking a balance between leveraging AI to enhance productivity and respecting individual privacy rights is essential (Source 6). By addressing these ethical concerns and biases, organizations can harness the full potential of AI while ensuring that its deployment aligns with values of fairness, transparency, and accountability.
Data Privacy and Security Issues
As artificial intelligence continues to transform workplaces, the issues of data privacy and security have emerged as critical concerns. With AI systems increasingly handling vast amounts of sensitive data, the potential for breaches and misuse has grown substantially. AI systems require access to large datasets to function effectively, often including personal and proprietary information. This necessity raises significant privacy concerns, as organizations must ensure that data is collected, stored, and processed in compliance with strict privacy regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States (Source A).
The integration of AI into business operations also means that data is often shared across multiple platforms and stakeholders, increasing the risk of unauthorized access. Cybersecurity measures must be robust and adaptive to protect against potential threats. AI itself can be both a tool for enhancing security and a target for cyberattacks. Machine learning algorithms can help identify and mitigate security threats in real-time, but they are also susceptible to adversarial attacks, where malicious actors manipulate input data to deceive AI systems (Source B).
Moreover, the transparency of AI processes is another critical aspect of data privacy and security. Understanding how AI systems make decisions is essential for ensuring accountability and trust. However, many AI models, especially deep learning networks, operate as “black boxes,” making it challenging to decipher how they process data and reach conclusions (Source C). This opacity can hinder efforts to identify and correct biases or errors in AI outputs, posing additional risks to data integrity and user safety.
In conclusion, as AI continues to permeate workplace environments, addressing data privacy and security issues is paramount. Organizations must adopt comprehensive strategies that encompass regulatory compliance, robust cybersecurity measures, and transparent AI practices to safeguard data and maintain trust (Source D).
The Need for Continuous Learning and Adaptation
In the rapidly evolving landscape of artificial intelligence (AI) in workplaces, the importance of continuous learning and adaptation cannot be overstated. As AI technologies advance from automation to augmentation, the skills required by the workforce are also transforming. This shift necessitates a proactive approach to learning, where employees continuously update their skills to keep pace with technological advancements and evolving job roles.
AI’s integration into workplaces has led to the emergence of new tasks that require a combination of human and machine capabilities. Employees are expected to develop not only technical skills to interact with AI tools but also soft skills such as critical thinking, creativity, and emotional intelligence, which machines cannot replicate (Source 1). This hybrid skill set is crucial for workers to effectively collaborate with AI systems and leverage their capabilities to enhance productivity and innovation.
Continuous learning is essential because the half-life of skills is shrinking; what was relevant five years ago might be obsolete today (Source 2). Organizations must foster a culture that encourages lifelong learning, providing employees with access to training programs and resources that support skill development. This includes upskilling and reskilling initiatives tailored to meet the specific needs of their workforce in an AI-augmented environment.
Moreover, adaptation is key to navigating the dynamic changes AI brings to the workplace. Employees and organizations must be agile, ready to pivot and embrace new ways of working as AI tools evolve (Source 3). This adaptability not only ensures that workers remain competitive in the job market but also empowers organizations to harness AI’s full potential, driving innovation and maintaining a competitive edge in their respective industries.
In conclusion, continuous learning and adaptation are indispensable in the transition from automation to augmentation. They equip both individuals and organizations to thrive in an AI-driven world, ensuring sustainable growth and success.
Preparing for the Future: Strategies for Businesses
In the evolving landscape of artificial intelligence (AI), businesses must adopt strategic approaches to harness the potential of AI not just for automation but for augmentation. This shift requires a proactive stance in preparing for future workplace dynamics. Firstly, investing in employee training and development is crucial. As AI technologies become more integrated into daily operations, employees will need new skills to work alongside these systems effectively. Businesses should focus on fostering a culture of continuous learning, ensuring that staff are equipped to leverage AI tools to enhance their productivity and decision-making capabilities (Source 1).
Additionally, companies should prioritize data literacy across their workforce. The ability to interpret and utilize data-driven insights is becoming increasingly important. By developing a workforce adept in data analysis and interpretation, businesses can better utilize AI technologies to augment human capabilities, leading to more informed strategic decisions and innovative solutions (Source 2).
Moreover, fostering a collaborative environment between humans and AI is essential. This involves rethinking job roles and workflows to maximize the strengths of both AI and human workers. By redesigning processes to allow AI to handle repetitive and data-intensive tasks, employees can focus on creative, strategic, and interpersonal functions that require human intuition and empathy (Source 3).
Finally, businesses should engage in ethical AI practices, ensuring transparency and fairness in AI applications. Establishing clear guidelines and ethical standards for AI use will not only build trust among employees and consumers but also safeguard against potential biases and misuse of technology. As AI continues to evolve, maintaining a human-centric approach will be key to its successful integration in the workplace (Source 4).
By implementing these strategies, businesses can effectively transition from automation to augmentation, preparing themselves for a future where AI acts as a powerful tool for enhancing human work rather than replacing it.
Investing in Employee Training and Development
In the rapidly evolving landscape of artificial intelligence and its integration into the workplace, investing in employee training and development has become a crucial strategy for businesses aiming to harness the full potential of AI technologies. As AI systems transition from automating routine tasks to augmenting human capabilities, the need for a workforce skilled in collaboration with these technologies is more pronounced than ever.
The adoption of AI in the workplace necessitates a shift in skills. Employees must be equipped not only with technical skills to interact with AI systems but also with critical thinking and problem-solving abilities to interpret AI-generated insights (Source 1). This dual focus ensures that employees can leverage AI to enhance their decision-making processes, rather than being overshadowed by the technology.
Furthermore, comprehensive training programs can alleviate employee anxiety about job displacement due to AI. By emphasizing development, businesses can foster a culture of continuous learning, where employees feel empowered to adapt and thrive alongside AI (Source 2). This empowerment is crucial in maintaining morale and engagement, which are vital for productivity and innovation.
Investing in employee development also aligns with the broader organizational goals of enhancing competitiveness and driving innovation. As employees become more adept at using AI tools, they can contribute to developing new processes and products, thereby adding value to the organization (Source 3). Moreover, companies that prioritize employee training are more likely to attract and retain top talent, as they are perceived as forward-thinking and supportive employers.
In conclusion, as AI continues to reshape the workplace, businesses must prioritize employee training and development. This investment not only equips the workforce with the necessary skills to work alongside AI but also positions companies to innovate and lead in an increasingly AI-driven world.
Building a Collaborative AI-Human Workforce
In the evolving landscape of artificial intelligence (AI) integration within workplaces, the focus is shifting from automation to augmentation, emphasizing the creation of a collaborative AI-human workforce. This shift recognizes that while AI can handle repetitive and data-intensive tasks, human intuition, creativity, and emotional intelligence remain irreplaceable. The synergy between AI and humans can lead to enhanced productivity and innovation, leveraging the strengths of both entities (Source A).
The first step in building a collaborative AI-human workforce is redefining roles to leverage AI’s analytical prowess alongside human insight. This involves creating hybrid roles where AI handles data processing and pattern recognition, allowing humans to focus on decision-making and strategic planning. For instance, in sectors like healthcare, AI can process large datasets to identify potential health risks, while doctors interpret these insights to devise personalized treatment plans (Source B).
Moreover, fostering a culture of continuous learning and adaptation is crucial. As AI technologies evolve, employees must be equipped with the skills to work alongside these systems. Organizations should invest in training programs that enhance digital literacy and promote an understanding of AI technologies. This will empower employees to use AI tools effectively and contribute to their integration within workflows (Source C).

Another important aspect is designing AI systems that are transparent and explainable. Employees are more likely to trust and collaborate with AI if they understand how decisions are made. Transparent AI fosters trust, facilitates better human oversight, and enhances collaborative outcomes (Source D).
Finally, organizations should prioritize ethical considerations in AI deployment, ensuring that these technologies augment rather than replace human roles. By focusing on ethical AI design and implementation, companies can create an environment where AI supports human workers, leading to a more balanced and productive workforce (Source E). This collaborative approach not only enhances operational efficiency but also fosters a more inclusive and dynamic workplace environment.
Embracing a Culture of Innovation and Change
In the transition from automation to augmentation within workplaces, embracing a culture of innovation and change is essential. Organizations must cultivate an environment where employees are encouraged to think creatively and adapt to new technologies. This cultural shift not only fosters innovation but also ensures that businesses remain competitive in an ever-evolving market.
To begin with, leadership plays a pivotal role in embedding a culture of innovation. Leaders should model adaptability and openness to change, demonstrating a willingness to experiment and take calculated risks. By doing so, they set a precedent that encourages employees to explore new ideas without fear of failure (Source A). Additionally, organizations can implement structured programs such as innovation labs or hackathons, which provide dedicated time and resources for employees to develop and test new concepts (Source B).
Moreover, continuous learning and development are crucial components of this cultural shift. Companies should invest in upskilling and reskilling programs that equip employees with the skills needed to work alongside AI technologies. This not only enhances employees’ ability to contribute to innovative projects but also increases their job satisfaction and engagement (Source C).
Furthermore, fostering a collaborative environment is key. Cross-functional teams should be encouraged to work together, combining diverse perspectives and expertise to drive innovation. This collaborative approach helps break down silos and promotes a more holistic view of problem-solving (Source D).
Finally, open communication is essential in nurturing a culture of innovation. Organizations should create platforms for employees to share ideas and feedback freely. Regular town halls, suggestion boxes, and digital forums can facilitate this exchange, ensuring that the best ideas are recognized and developed (Source E).
By embracing a culture of innovation and change, organizations can effectively transition from automation to augmentation, leveraging AI to enhance human capabilities and drive business success.
Conclusion
In the rapidly evolving landscape of artificial intelligence (AI) within workplaces, the transition from automation to augmentation represents a pivotal shift. This transition underscores the increasing role of AI not as a substitute for human labor but as a complement that enhances human capabilities. As AI technologies continue to mature, their integration into the workplace is poised to redefine job roles, improve productivity, and foster innovation.
The augmentation of human tasks with AI tools allows for a symbiotic relationship where AI handles repetitive and data-intensive tasks, freeing human workers to focus on more complex, creative, and interpersonal aspects of their jobs. This collaboration can lead to higher job satisfaction and performance, as employees are empowered to leverage AI’s strengths in data processing and analysis while applying their unique human insights to decision-making processes (Source 1).
Moreover, as AI becomes more embedded in workplace operations, it is crucial for organizations to invest in upskilling and reskilling their workforce. This investment ensures that employees can effectively interact with AI systems and harness their full potential, thereby maximizing the benefits of AI augmentation (Source 2). Furthermore, fostering a culture of continuous learning will be essential for maintaining a competitive edge in an AI-driven market.
While the potential of AI-driven augmentation is immense, it also necessitates addressing ethical considerations such as bias, transparency, and the impact on employment. Organizations must navigate these challenges by establishing robust governance frameworks that prioritize fairness and accountability (Source 3).
In conclusion, the shift from automation to augmentation in workplaces marks an exciting new phase in the integration of AI. By embracing this evolution, businesses can unlock unprecedented opportunities for innovation and growth, while also ensuring that their workforce remains adaptable and engaged in an AI-enhanced future (Source 4).
The Future of AI in Workplaces: A Balanced Approach
The future of AI in workplaces is poised to adopt a balanced approach, where the focus shifts from merely automating tasks to enhancing human capabilities. This transformation is driven by the realization that while AI can efficiently handle routine and data-driven tasks, the human touch is indispensable for creativity, empathy, and complex problem-solving. As businesses integrate AI technologies, they are increasingly looking to create symbiotic environments where AI tools augment human work rather than replace it (Source A).
One key aspect of this balanced approach is the redefinition of roles within organizations. As AI takes over mundane tasks, employees are freed to engage in more strategic and creative activities. This shift not only boosts productivity but also enhances job satisfaction, as workers are able to focus on more meaningful contributions (Source B). Moreover, AI’s ability to process vast amounts of data can aid in decision-making processes, providing insights that humans might overlook, thus complementing human judgment with data-driven intelligence.
Furthermore, the future workplace will likely emphasize continuous learning and adaptability. As AI technologies evolve, so too must the skills of the workforce. Organizations will need to invest in training programs to help employees develop new skills that complement AI capabilities, such as critical thinking, emotional intelligence, and advanced data analysis (Source C).
Another significant consideration is the ethical deployment of AI. Companies must ensure transparency in AI operations and address potential biases in algorithms to foster trust among employees and customers alike (Source D). By aligning AI implementation with ethical guidelines, businesses can create a harmonious environment where technology and human ingenuity thrive together.
In summary, the future of AI in workplaces lies in a balanced approach that leverages AI to empower human workers, thereby driving innovation and maintaining human-centric values in business operations.
Encouraging Responsible and Ethical AI Practices
The integration of AI in workplaces necessitates a shift towards responsible and ethical practices to ensure technology benefits society as a whole. As AI continues to augment human capabilities, the focus must be on developing systems that align with ethical guidelines and societal values.
Firstly, transparency in AI systems is crucial. Organizations need to ensure that AI algorithms are understandable and their decision-making processes are clear to users. This transparency fosters trust and accountability, allowing stakeholders to scrutinize AI outcomes and address biases or errors promptly (Source 1). By making AI systems more interpretable, companies can mitigate risks associated with opaque decision-making processes that could lead to discrimination or unfair treatment.
Moreover, implementing robust data governance frameworks is essential. AI systems are heavily reliant on data, and ensuring data quality, privacy, and security is paramount. Organizations must adopt practices that protect user data and comply with regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). Ensuring that AI systems use ethically sourced and unbiased data sets can prevent the perpetuation of historical biases and promote fairness (Source 2).
Additionally, fostering a culture of ethical AI usage requires ongoing education and training for employees. Companies should invest in training programs that raise awareness about the ethical implications of AI and equip employees with the skills to responsibly develop and manage AI technologies (Source 3). Encouraging a workforce that is knowledgeable about AI ethics can lead to more conscientious decision-making and innovation.
Finally, collaboration with diverse stakeholders, including ethicists, policymakers, and affected communities, is vital. Engaging with a broad range of perspectives can help identify potential ethical dilemmas and develop inclusive AI systems that cater to the needs of all users (Source 4). By prioritizing responsible and ethical AI practices, organizations can harness the full potential of AI while safeguarding human values and societal well-being.

FAQs
- What is the difference between automation and augmentation in the context of AI in workplaces?
Automation refers to the use of AI to perform tasks without human intervention, often replacing human labor for efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Augmentation, on the other hand, involves AI systems enhancing human capabilities, allowing workers to perform their jobs more effectively and creatively by providing them with advanced tools and insights (Source 1).
- How is AI expected to change the nature of jobs in the future?
AI is projected to transform jobs by shifting the focus from routine, repetitive tasks to more complex problem-solving and creative work. This transition is expected to foster new roles that emphasize human skills such as emotional intelligence, critical thinking, and strategic decision-making. As AI handles more of the operational aspects, employees can concentrate on tasks that require human intuition and innovation (Source 2).
- What industries are most likely to benefit from AI augmentation?
Industries with a high degree of data-driven decision-making, such as healthcare, finance, and manufacturing, are poised to benefit significantly from AI augmentation. In healthcare, for instance, AI can assist doctors by analyzing vast amounts of medical data to provide more accurate diagnoses. In finance, AI tools can enhance risk assessment and fraud detection, while in manufacturing, AI can optimize production processes and predictive maintenance (Source 3).
- What are the challenges associated with implementing AI augmentation in workplaces?
One of the main challenges is the need for significant investment in training employees to work effectively alongside AI systems. Additionally, integrating AI into existing workflows may require restructuring and overcoming resistance to change. There is also the ethical consideration of ensuring that AI systems are used responsibly and do not perpetuate biases or infringe on privacy (Source 4).
- How can organizations prepare for the transition from automation to augmentation?
Organizations can prepare by investing in upskilling their workforce, fostering a culture of continuous learning, and developing strategic plans that align AI initiatives with business goals. It’s essential for companies to engage in open communication about the benefits and challenges of AI and to involve employees in the process of integrating AI into their roles (Source 5).
What is the difference between AI Automation and Augmentation?
AI automation and augmentation represent two distinct approaches to integrating artificial intelligence into workplace processes, each with unique implications for how tasks are performed and jobs are structured.
AI automation refers to the use of technology to perform tasks without human intervention. This approach focuses on replacing repetitive, rule-based activities that can be executed with precision and efficiency by machines. Automation is particularly effective in areas such as data entry, basic customer service inquiries, and routine manufacturing processes, where tasks follow predictable patterns (Source 1). The primary objective of AI automation is to enhance productivity by reducing human involvement in mundane and time-consuming tasks, thereby minimizing errors and lowering operational costs (Source 2).
In contrast, AI augmentation involves the use of AI to enhance human capabilities and decision-making rather than replace them. Augmentation aims to empower employees by providing them with advanced tools and insights that improve their productivity and effectiveness. For example, AI-driven analytics can help professionals in fields such as finance or healthcare make more informed decisions by processing vast datasets quickly and accurately (Source 3). Augmentation promotes a collaborative relationship between humans and machines, where AI acts as an assistant that supports and enhances human skills, creativity, and strategic thinking (Source 4).
The key difference between the two lies in their approach to human involvement: automation seeks to minimize it, while augmentation aims to optimize it. As businesses increasingly recognize the value of human insight and creativity, the trend is shifting towards augmentation, which emphasizes a synergistic partnership between humans and AI, leading to more innovative and adaptable workplaces (Source 5).
How can businesses start implementing AI augmentation?
To begin implementing AI augmentation, businesses should start by identifying areas where AI can complement human capabilities and enhance productivity. The first step is to conduct a thorough needs assessment to understand which processes can benefit from AI technologies. This involves analyzing workflows to pinpoint repetitive tasks that can be automated, thereby allowing employees to focus on more strategic activities (Source A).
Next, companies should invest in the right AI tools that align with their specific industry needs. For instance, customer service departments might benefit from AI-driven chatbots, while manufacturing sectors could implement AI for predictive maintenance. It’s essential that businesses choose scalable AI solutions that can grow with the company’s needs (Source B).
Additionally, businesses must focus on data management. AI systems require high-quality data to function effectively, so organizations should prioritize data collection and management practices to ensure accuracy and accessibility (Source C). This includes investing in data storage solutions and establishing data governance policies to maintain data integrity.
Training and development are also crucial. Employees should be educated about AI technologies and their potential impacts on their roles. By providing training sessions and workshops, companies can ensure that their workforce is equipped with the necessary skills to work alongside AI systems (Source D).
Furthermore, fostering a culture of innovation and openness to change will help smooth the transition. Encouraging feedback and collaboration between human employees and AI systems can lead to more effective implementation and continuous improvement (Source E).
Finally, businesses should start small and scale up. Piloting AI solutions in specific departments before a full-scale rollout allows companies to test the effectiveness of AI augmentation and make necessary adjustments (Source F). This methodical approach minimizes risks and maximizes the potential benefits of AI integration.
What are the potential risks of AI augmentation in the workplace?
AI augmentation in the workplace presents a plethora of potential risks that must be carefully considered and managed to ensure successful integration and ethical practices. One of the primary concerns is the risk of job displacement. While AI augmentation aims to enhance human capabilities rather than replace them, there is still a significant fear that certain jobs may become obsolete, particularly those involving repetitive or routine tasks. This could lead to increased unemployment rates and economic disparity if proper measures, such as retraining and upskilling, are not implemented to transition workers into new roles (Source 1).
Another risk involves privacy and data security. AI systems often require access to vast amounts of sensitive data to function effectively. This raises concerns about how this data is collected, stored, and used, potentially leading to breaches of privacy or misuse of personal information (Source 2). Organizations must ensure robust data protection measures are in place to mitigate these risks.
Bias and fairness are also significant issues with AI systems. If AI models are trained on biased data, they can perpetuate or even exacerbate existing biases, leading to unfair treatment of certain groups of people in the workplace. This can affect hiring, promotions, and performance evaluations, thereby reinforcing systemic inequalities (Source 3).
Moreover, there is the risk of over-reliance on AI systems, which could diminish human skills and judgement over time. Employees might become too dependent on AI for decision-making, potentially leading to a loss of critical thinking skills and an inability to function effectively without technological support (Source 4).
Finally, ethical considerations surrounding AI deployment must be addressed. The lack of transparency in how AI models make decisions can lead to accountability issues, where it becomes challenging to determine who is responsible for decisions made by AI-augmented systems (Source 5). Addressing these risks requires a balanced approach that involves continuous monitoring, ethical guidelines, and comprehensive training programs to ensure AI augmentation benefits all stakeholders in the workplace.